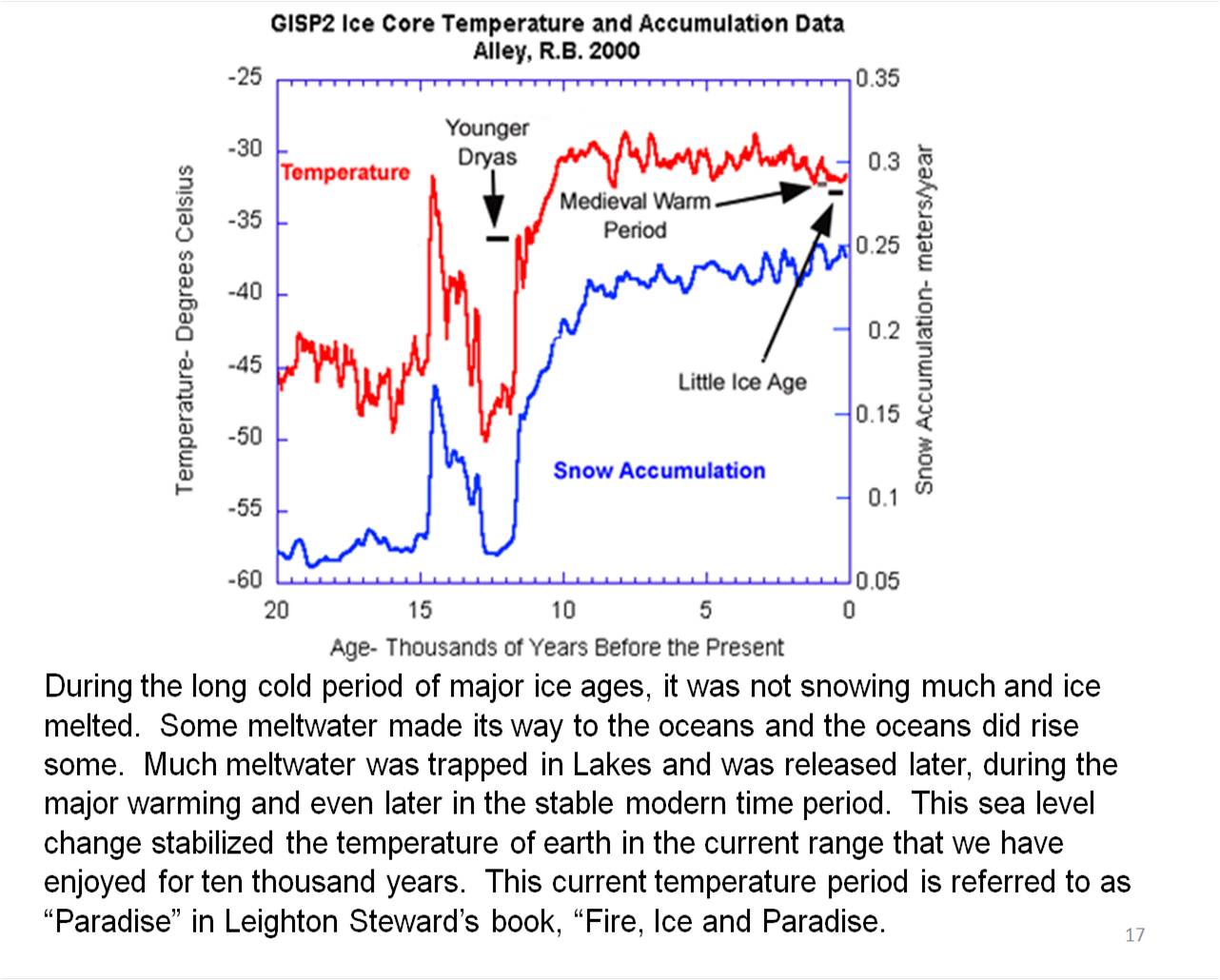
Lake Bonneville filled up with meltwater during the long cold period and broke through to the Pacific, leaving the Great Salt Lake as the remains. Lake Agassiz, [ag-uh-see; also Fr. a-g a-see] a large meltwater lake, at the edge of the Laurentide Ice Sheet in Canada and the US, burst through an ice dam during the last major warming and suddenly emptied, most likely to the North down the Mackenzie River into the Arctic Ocean. Another huge glacial lake in Siberia, larger than Lake Agassiz, broke out during the last major warming. This was at the time of the famous Younger Dryas event and these water releases were the causes of The Younger Dryas cooling. There are other of these water dumps. These events returned earth to ice age temperatures and stalled the last major warming period for a couple thousand years or more. Lake Agassiz dumped more meltwater again in the 8.2ka event and is no longer recognized as a current major lake. These events raised the levels of the oceans to the point that warming events could not cause enough snow to lower the oceans to the point of cutting of ocean flow into the Arctic, as Ewing and Donn explained in their ice age and global warming theory. Climate was then stabilized in the current range that we have enjoyed for ten thousand years.